Logit
Logit is the logistic equivalent deviate. It is a specific transformation of data that can be applied to the proportions of test organisms affected in a quantal toxicity test, usually resulting in a straightening of the sigmoid curve of effect. To obtain a logit, the proportion of organisms affected (p) at a given concentration is divided by (1-p). The logarithm of the result is then taken, and that value is the logit (Environment Canada, 2005).
The logit method, similar to the probit method, must include two partial effects between 0% and 100% effect in the data. Probit or logit regression is a commonly used and satisfactory approach for analyzing quantal data. Logits are mathematically superior, but probits have been widely used in environmental toxicology.
Advantages of Logits (Environment Canada, 2005)
The analysis of quantal data with logit is superior to using probit for several reasons:
- It is numerically more stable than probit estimates, with a lower likelihood of failure (Hoekstra, 1989).
- The parameters produced by logistic regression utilize all relevant information from a series of observations, which is not the case with probit regression. Conversely, the parameters of a logistic regression have a direct meaning in reconstructing the original data.
- The parameters of the logistic model are widely used in biomedical literature as measures of risk.
- Computer programs are somewhat easier to develop for logistic regression models.
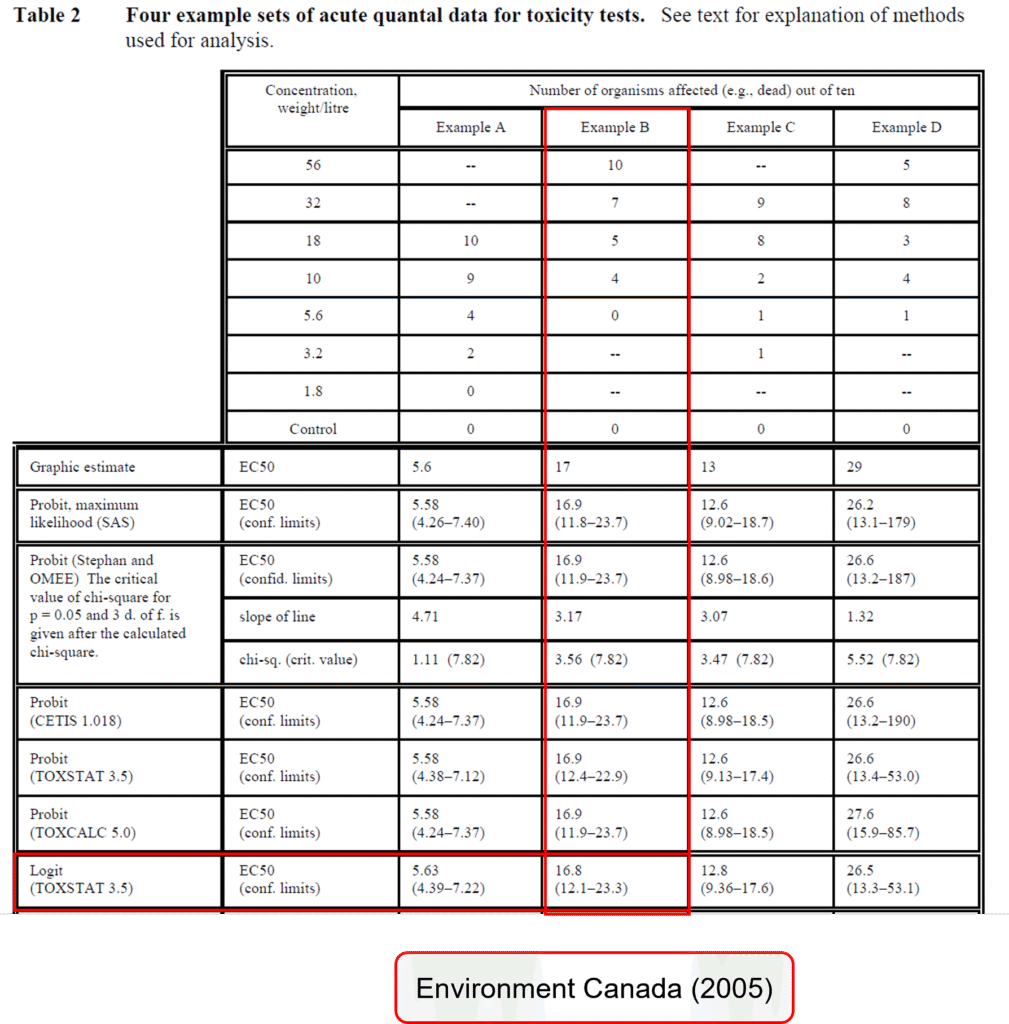
Analysis Results of ToxGenie’s Logit Method
To compare ToxGenie’s analysis results, the Logit Method was applied using the same data as in the Environment Canada Report (EPS 1/RM/46 – March 2005). The results are presented below.
Due to differences in the number of decimal places used in mathematical calculations and the criteria for rounding, the results are not entirely identical to those of the Environment Canada (2005) analysis. For point estimation analysis, ToxGenie recommends the Maximum Likelihood Estimation (MLE) of the Probit Method for Environment Canada’s data. However, if the user does not apply the recommended analysis method, ToxGenie can also perform the analysis using a user-specified method.
Start Your Toxicology Data Statistical Analysis with ToxGenie
Understanding quantal and quantitative data is the first step toward robust toxicology research. ToxGenie offers an intuitive platform for both data types, making it ideal for beginners and experts alike. Interested? Start with a 30-day free trial and revolutionize your toxicology data statistical analysis today!