Spearman-Kärber Method
Introduced by Hamilton et al. (1977) for environmental toxicity testing, the Spearman-Kärber Method (S-K) is recommended for analyzing quantal data when (a) there is only one partial effect and (b) both 0% and 100% effects are included. In other words, this method is used when probit/logit methods are not applicable, i.e., when the data do not include two partial effects between 0% and 100%.
While most commercial software programs offer the Spearman-Kärber Method, it appears to have procedural flaws in certain cases of irregular data, which is best avoided. The Spearman-Kärber Method takes a mathematical approach that is significantly different from probit regression. It estimates LC50, EC50, and LD50 by using a weighted average of the midpoints between concentrations on a logarithmic scale. The weight applied to each midpoint is the change in the effect proportion between the two concentrations. This concept is similar to estimating the mean of a frequency distribution, where class midpoints are multiplied by their corresponding proportions.
The Spearman-Kärber Method can handle uneven intervals of concentrations on a logarithmic scale and varying numbers of test organisms at different concentrations. Additionally, it does not have a specific method for addressing effects in the control group. Confidence intervals can be estimated when at least one partial effect is present, calculated as the estimated LC50, EC50, or LD50 ± 2 standard deviations (SD), assuming the estimate is accurate.
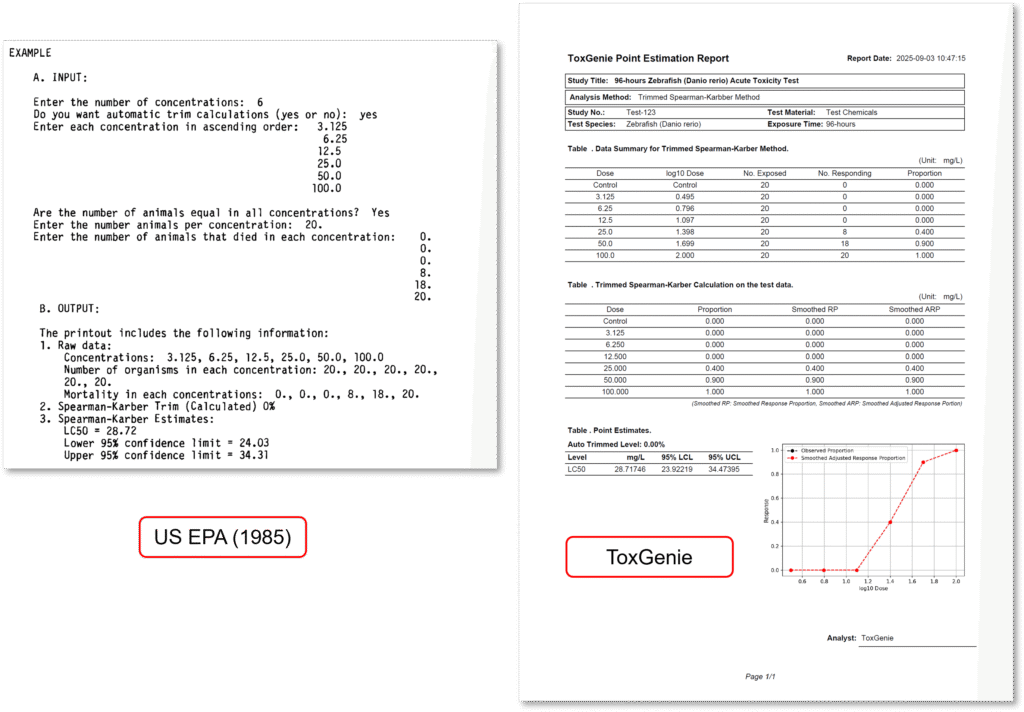
Analysis Results of ToxGenie’s Spearman-Kärber Method
To compare ToxGenie’s analysis results, the Spearman-Kärber Method was applied using the same data as in the US EPA Report (EPA 600/4-85-013, 3rd edition, 1985). The results are shown in the figure above.
Due to differences in the number of decimal places used in mathematical calculations and the criteria for rounding, the results are not entirely identical to those of the US EPA analysis. However, they demonstrate highly accurate calculations. For point estimation analysis, ToxGenie recommends the Logit Method for the US EPA data. However, if the user does not apply the recommended analysis method, ToxGenie can also perform the analysis using a user-specified method.
Start Analyzing with ToxGenie
ToxGenie simplifies complex toxicology data analysis, making it ideal for both beginners and seasoned researchers. Experience it firsthand with a 30-day free trial. Take the first step toward revolutionizing your toxicology research with ToxGenie!